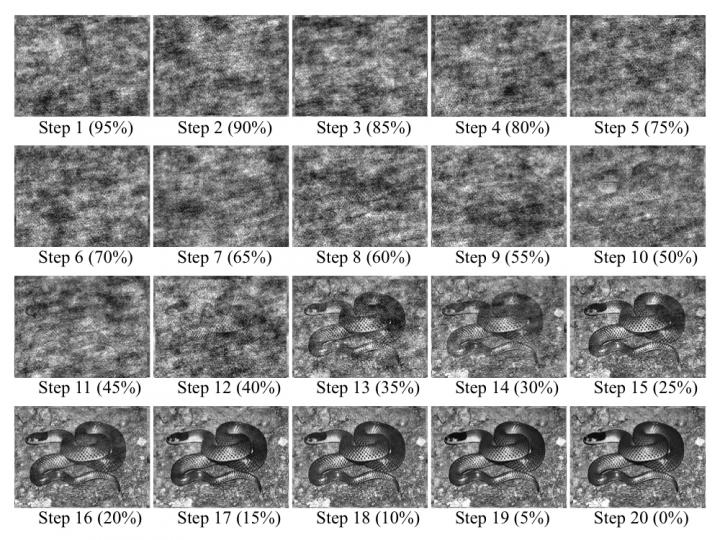
Credit: Nobuyuki Kawai
Nagoya, Japan – Some studies have suggested that the visual systems of humans and other primates are finely tuned to identify dangerous creatures such as snakes and spiders. This is understandable because, among our ancestors, those who were more able to see and avoid these animals would have been more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation. However, it has been difficult to compare the recognition of different animals in an unbiased way because of their different shapes, anatomical features, and levels of camouflage.
In a study reported recently in PLOS ONE, a pair of researchers at Nagoya University obtained strong support for the idea that humans have heightened visual awareness of snakes. The researchers applied an image manipulation tool and revealed that subjects could identify snakes in much more blurry images than they could identify other harmless animals in equivalent images.
The tool, called Random Image Structure Evolution (RISE), was used to create a series of 20 images of snakes, birds, cats, and fish, ranging from completely blurred to completely clear. The pair then asked subjects to views these images in order of increasing clarity until they could identify the animal in the picture.
"Because of the algorithm that it uses, RISE produces images that allow unbiased comparison between the recognition of different animals," first author Nobuyuki Kawai says. "In the images, the animals are 'camouflaged' in a uniform way, representing typical conditions in which animals are encountered in the wild."
The snakes were increasingly well-identified in the sixth to eighth of 20 images, while the subjects often needed to see the less blurred ninth or tenth images to identity the other animals. "This suggests that humans are primed to pick out snakes even in dense undergrowth, in a way that isn't activated for other animals that aren't a threat," co-author Hongshen He explains.
The findings confirm the Snake Detection Theory; namely, that the visual system of humans and primates has specifically evolved in a way that facilitates picking out of dangerous animals. This work augments understanding of the evolutionary pressures placed on our ancestors.
###
The article "Breaking Snake Camouflage: Humans Detect Snakes More Accurately than Other Animals under Less Discernible Visual Conditions" was published in PLOS ONE at DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164342
Media Contact
Koomi Sung
[email protected]
http://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/