Credit: Maxime Derex
Are the technologies produced by human civilisations the result of our intellectual abilities or our capacity for imitation? According to an international team consisting of researchers from the University of Exeter, the Université catholique de Lille, the CNRS and Arizona State University, with support from the TSE at Toulouse 1 Capitole university (1), the creation of effective technologies does not necessarily require an understanding of them.
It is often believed that humans succeeded in producing complex tools and adapting to different environments thanks to their impressive brain, which makes them more ingenious and inventive than other species. Yet the effectiveness of traditional technologies such as bows or kayaks depends on numerous parameters that remain difficult to understand and model, even for modern physicists. Some anthropologists have consequently suggested that these technologies result not from our reasoning abilities, but from our propensity to copy other members of our group: small improvements are successively selected, leading to the emergence of technologies that are effective despite not being understood by individuals.
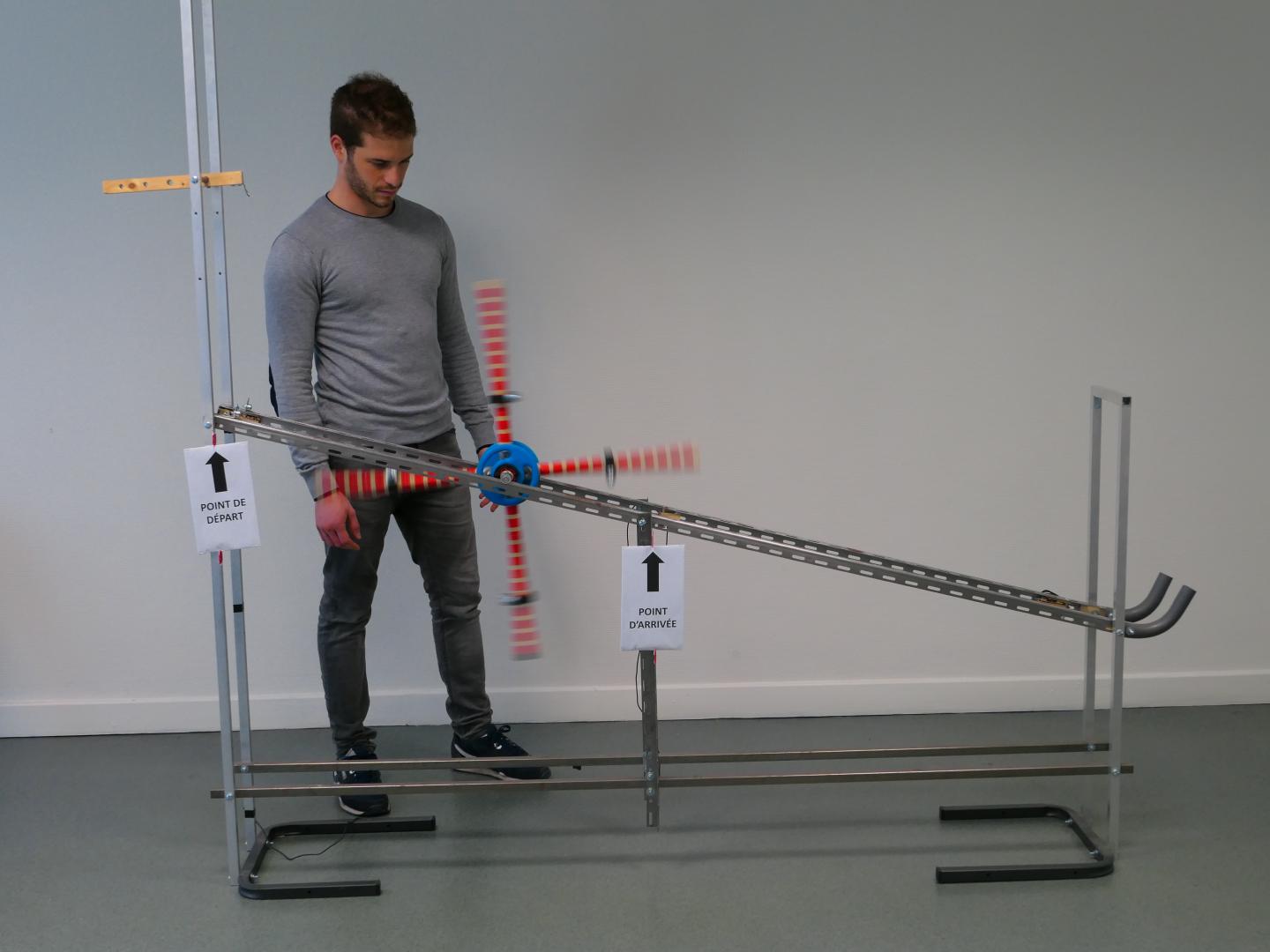
Researchers sought to test this theory in the laboratory. In order to do so, they recruited students to optimise a wheel traveling down on rails (photo). They were each given five attempts to produce the most effective configuration, before responding to a questionnaire that tested their understanding of the physical mechanisms that impact the wheel’s speed. In order to simulate the succession of human generations, researchers created chains of five individuals: each of them had access on a computer screen to the wheel’s configuration and effectiveness from the final two attempts made by the preceding participant.
As the wheel increased in speed over the course of “generations,” the understanding of individuals remained mediocre. In other words, there was no link between the wheel’s performance and the participants’ level of understanding! Each individual produced more or less random configurations, and the combination of these individual trials and errors and of the copying of the fastest configurations proved sufficient for optimising the wheel.
In a second version of the experiment, the participants transmitted their final two attempts to the following individual, as well as a text describing their theory on the wheel’s effectiveness. The results were similar, with the wheels gaining in speed, although once again without the individuals understanding why. The transmission of false or incomplete theories could even prevent subsequent generations from developing a proper understanding of the system, in a way blinding them to a part of the problem.
This experiment illustrates the importance of cultural processes in the emergence of complex tools, as our ability to copy other individuals enables the emergence of technologies that no single individual could have invented alone. It also encourages us to be more prudent in the interpretation of archaeological remains in terms of cognitive capacities, as these abilities are not the only driver of technological evolution.
###
Notes
(1) Maxime Derex is a researcher at the University of Exeter and a member of the ETHICS laboratory at the Université catholique de Lille. Jean-François Bonnefon is a CNRS researcher at the Toulouse School of Management Research laboratory (CNRS/Université Toulouse 1 Capitole), as well as a member of the TSE (Toulouse School of Economics).
Media Contact
Veronique Etienne
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.



