Theoretical approach for assembling nanoparticles uses an idea similar to separated vinaigrettes
Credit: Gaurav Arya, Duke University
DURHAM, N.C. — Materials scientists at Duke University have theorized a new “oil-and-vinegar” approach to engineering self-assembling materials of unusual architectures made out of spherical nanoparticles. The resulting structures could prove useful to applications in optics, plasmonics, electronics and multi-stage chemical catalysis.
The novel approach appeared online on March 25 in the journal ACS Nano.
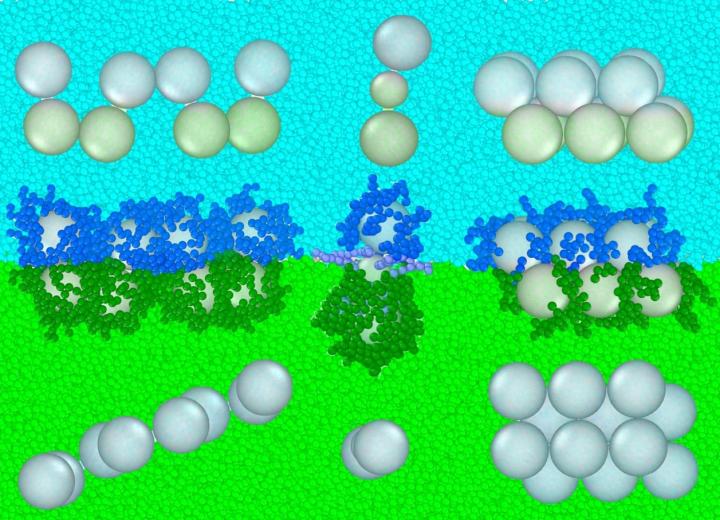
Left to their own tendencies, a system of suspended spherical nanoparticles designed to clump together will try to maximize their points of contact by packing themselves as tightly as possible. This results in the formation of either random clusters or a three-dimensional, crystalline structure.
But materials scientists often want to build more open structures of lower dimensions, such as strings or sheets, to take advantage of certain phenomena that can occur in the spaces between different types of particles. And they’re always on the lookout for clever ways to precisely control the sizes and placements of those spaces and particles.
In the new study, Gaurav Arya, associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at Duke, proposes a method that takes advantage of the layers formed by liquids that, like a bottle of vinaigrette left on the shelf for too long, refuse to mix together.
When spherical nanoparticles are placed into such a system, they tend to form a single layer at the interface of the opposing liquids. But they don’t have to stay there. By attaching “oil” or “vinegar” molecules to the particles’ surfaces, researchers can make them float more on one side of the dividing line than the other.
“The particles want to maximize their number of contacts and form bulk-like structures, but at the same time, the interface of the different liquids is trying to force them into two layers,” said Arya. “So you have a competition of forces, and you can use that to form different kinds of unique and interesting structures.”
Arya’s idea is to precisely control the amount that each spherical nanoparticle is repelled by one liquid or the other. And according to his calculations, by altering this property along with others such as the nanoparticles’ composition and size, materials scientists can make all sorts of interesting shapes, from spindly molecule-like structures to zig-zag structures where only two nanoparticles touch at a time. One could even imagine several different layers working together to arrange a system of nanoparticles.
In the proof-of-concept paper, the nanoparticles could be made out of anything. Gold or semiconductors could be useful for plasmonic and electrical devices, while other metallic elements could catalyze various chemical reactions. The opposing substrates that form the interface, meanwhile, are modeled after various types of polymers that could also be used in such applications.
“So far in this paper, we have only introduced the assembly approach and demonstrated its potential to create these exotic arrangements that you wouldn’t normally get,” said Arya. “There are so many more things to do next. For one, we’d like to explore the full repertoire of possible structures and phases researchers could make using this concept. We are also working closely with experimentalists to test the full capabilities of this approach.”
###
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (CMMI Award 1636356, ACI-1053575).
CITATION: “Interfacial Assembly of Tunable Anisotropic Nanoparticle Architectures,” Tsung-Yeh Tang, Yilong Zhou, and Gaurav Arya. ACS Nano, March 25, 2019. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08733
Media Contact
Ken Kingery
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




