Researchers have combined data from genetic studies and revealed 28 new genomic regions associated with type 2 diabetes, some variants of which are not found in other ethnic groups
Credit: Suzuki et al. (2019) Nature Genetics
Osaka, Japan – The genetic and genomic revolutions have led to an abundance of data about the genetic factors that confer a predisposition to type 2 diabetes (T2D), alongside environmental and lifestyle-related causes. However, most of the studies were based on individuals of European descent, meaning that the findings, and any treatments based on them, may not be optimal for other ethnic groups.
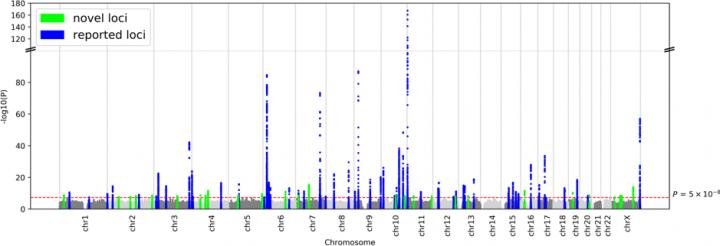
A new study performed by researchers from Osaka University, The University of Tokyo, RIKEN, and others and published in the journal Nature Genetics has shed more light on the genetics of diabetes in the Japanese population by analyzing data on over 36,000 sufferers of T2D and over 150,000 controls of Japanese ancestry. Their work has revealed 28 novel genomic regions associated with T2D, as well as related molecular pathways and cells, with some of these associations being specific to individuals of Japanese descent.
The team conducted a type of study called a meta-analysis, which involves combining the data from a number of independent studies in order to increase the amount of available data and thus the statistical power. As shown by this new study, this approach can potentially provide novel findings that aren’t unearthed by constitutive studies, each with a smaller sample size.
“We incorporated the data on links between type 2 diabetes and over 12 million variants across the whole genome from four different genome-wide association studies in the Japanese population,” Yukinori Okada says. “We found 88 genomic regions significantly associated with this disease, including 28 new ones, some of which are not found in European populations in previous reports.”
The group then looked in more detail at the identified genes, the effects of mutations on them and the proteins they encode, along with the associated pathways and cells. Examples of genetic factors linked to T2D include mutations in the GLP1R, involved in glucose-dependent insulin secretion, and in the genes CPA1 and GP2, known to help certain pancreatic cells transform into insulin-producing beta cells. Although the mutant forms of these genes were linked to T2D in this study, these mutations actually do not exist or are extremely rare in previous reports on European populations.
“Our findings indicate that some of the genetic underpinnings and molecular pathways of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population may differ from those in European populations, which is unsurprising considering that, when comparing individuals of the same body mass index, Japanese are more prone to this disease,” lead author Ken Suzuki says. “Our work could lead to Japanese- or Asian-specific therapeutic measures being developed to more effectively prevent or treat diabetes in this ethnic group.”
###
The article “Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population” is published in Nature Genetics at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




