Credit: Department of Molecular Oncology,TMDU
A research team based at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) has used an integrated data analysis to classify hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer, into three distinct subgroups, which should aid targeted treatment
Tokyo, Japan – Liver cancer remains a major problem in healthcare globally, being the second most common cause of cancer-related death globally. Previous studies showed that this disease, especially its predominant form hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), exhibits substantial heterogeneity. However, efforts to categorize HCC more precisely have been limited by an inability to integrate data from various sources into a single classification system.
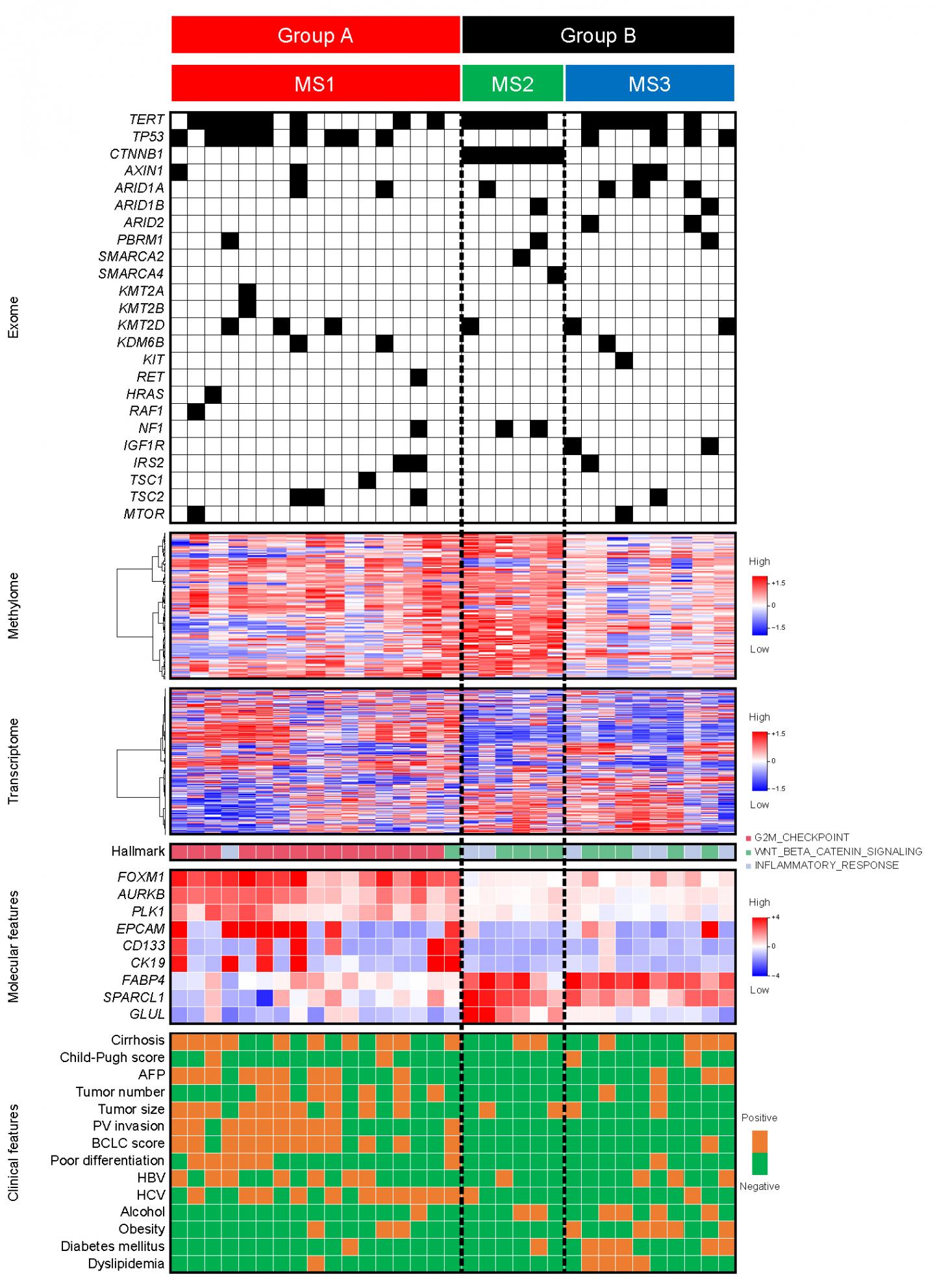
A Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU)-centered research group has made a major advance in this field by combining data on mutations, gene expression patterns, and immunological status to shed light on the variation among cases of HCC. The study, recently reported in the journal EBioMedicine, reveals that there are actually three distinct types of this disease, which should help in predicting the prognosis of individual patients and treating them more effectively (Fig 1).
The team first extracted a range of data on 183 removed HCC tumor specimens and then used statistical analysis to see if they clustered together into specific groups with distinct features. They then tested whether their findings were supported by an additional analysis of data from 373 HCC patients, and also incorporated data on each patient’s characteristics such as their clinical course and overall outcome.
“We knew that we’d have to take a large number of different variables into account in order to establish clinically useful stratification of HCC,” corresponding author Shinji Tanaka says. He adds, “our combination of genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic data and immune system characterization provided new insights into this disease.”
Among the three types of HCC revealed by the observations, one included tumors with mutation in the CTNNB1 gene along with a suppressed immune system (Fig 2). Another featured tumors in those with metabolic disease, associated with conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, rather than having an association with hepatitis virus infection as typically found in other cases. Finally, in the third group, the tumors showed mitogenic features and chromosomal instability, and a worse patient prognosis (Fig 3).
“If we can use this new classification to group HCC patients according to their subtype, it should help us provide the specific treatment that’s best for them,” lead author Shu Shimada of TMDU says. “Our finding of a metabolic disease-related subtype is also particularly important given the rate at which diseases such as obesity and diabetes are becoming more and more prevalent.”
The article “Comprehensive molecular and immunological characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma” is published in EBioMedicine at doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.058.
###
Media Contact
Shinji TANAKA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




