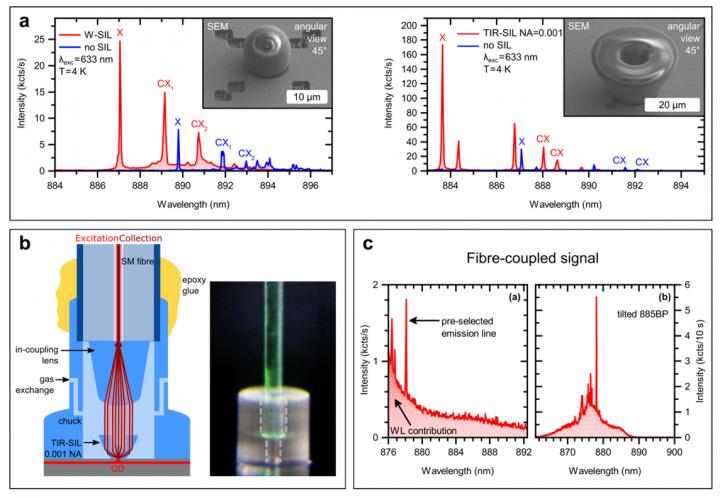
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by, Professor Harald Giessen and Professor Peter Michler from the 4th Physics Institute and the Institut für Halbleiteroptik und Funktionelle Grenzflächen, University of Stuttgart, Germany, and co-workers have worked on enhancing the extraction efficiency of semiconductor QDs by optimising micrometre-sized solid-immersion lens (SIL) designs. Two state-of-the-art technologies, i.e., low-temperature deterministic lithography and femtosecond 3D direct laser writing, are used in combination to deterministically fabricate micro-lenses on pre-selected QDs. Because of the high flexibility of 3D direct laser writing, various SIL designs, including hemispherical SILs (h-SILs), Weierstrass SILs (W-SILs), and total internal reflection SILs (TIR-SILs), can be produced and compared with respect to single-photon extraction enhancement. The experimentally obtained values are compared with analytical calculations, and the role of misalignment between SIL and QD as an error source is discussed in detail.
Furthermore, they highlight the implementation of an integrated single-mode fibre-coupled single-photon source based on 3D printed micro-optics. A 3D printed fibre chuck is used to precisely position an optical single-mode fibre onto a QD with a micro-lens printed on top. This fibre is equipped with another specifically designed 3D printed in-coupling lens to efficiently guide light from the TIR-SIL into the fibre core.
The main results presented in this paper are two-fold:
- A reproducible method to enhance the collection efficiency of single QDs based on 3D printed micro-lenses is presented. For all lens geometries, an increase in the collection efficiency was confirmed. The simplest geometry, namely h-SIL, resulted in an intensity enhancement of approximately 2.1. A further increase of up to approximately 3.9 in collection efficiency is promised by the hyperhemispherical Weierstrass geometry. The highest values were achieved for the total internal reflection geometries which reliably provide a PL intensity ratio between 6 and 10.
- A standalone a fibre-coupled standalone quantum dot device was realised. The validation of the approach for fibre in-coupling, that is the use of a QD provided with a TIR-SIL and a fibre with an additional focusing lens, was performed, employing a setup capable of precisely aligning the fibre with respect to the emitter. A value of up to 26?±?5% was shown, opening the route to a stable stand-alone, fibre-coupled device.
In the future, this technology can be combined with a QD single-photon source based on circular Bragg gratings, NV centres, defects, and a variety of other quantum emitters. In addition, a highly efficient combination with single quantum detectors should be feasible.
###
Media Contact
Harald Giessen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.