They published their work on July. 4th in Energy Material Advances.
Credit: Qingya Guo, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
They published their work on July. 4th in Energy Material Advances.
“The development of high-energy-density and safe all-solid-state lithium batteries employing solid electrolytes is imperative,” said paper author Xiayin Yao, professor with the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). “The cell-level energy density of all-solid-state lithium batteries highly depends on the thickness of solid electrolytes and inorganic solid electrolyte thin film generally show thick and rigid nature.”
Yao explained that polymer-in-ceramic garnet-based electrolytes can substantially overcome the above-mentioned challenges of garnet-type ceramic electrolytes.
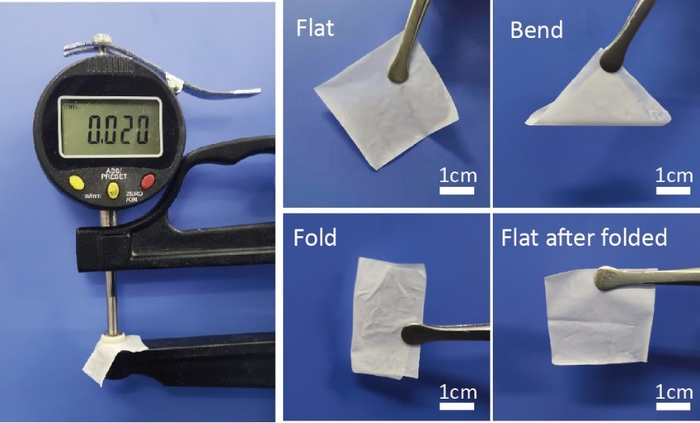
“Polymer-in-ceramic garnet-based solid electrolyte can combine the merits of flexibility of polymer component and excellent electrochemical stability, mechanical modulus and thermal stability of inorganic electrolytes,” Yao said. “However, due to the inferior strength of polymer component, polymer-in-ceramic garnet-based solid electrolyte generally show brittle fracture by reducing their thickness under high inorganic contents. Besides, traditional polymer-in-ceramic garnet-based solid electrolytes are often prepared by slurry casting method, which involves evaporation of massive noxious solvents and generally suffers sedimentation of agglomerated inorganic particles during preparation process.”
Yao and his team developed a 20 μm-thick flexible Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12 (LLZTO)-based solid electrolyte with 90 wt% LLZTO content through solvent-free procedure. The resultant 20μm-thick LLZTO-based film exhibits ultrahigh ionic conductance of 41.21 mS at 30 oC, excellent oxidation stability of 4.6 V, superior thermal stability and non-flammability. Moreover, the corresponding Li||Li symmetric cell can stable cycle for more than 2000 h with low overpotential at 0.1 mA cm-2 under 60 oC.
“The feasibility of the LLZTO-based film in all-solid-state lithium metal battery has been verified. The assembled Li||LiFePO4 pouch cell with integrated electrolyte/cathode interface exhibits excellent rate performances and cycle performances with a capacity retention of 71.4 % from 153 mAh g-1 to 109.2 mAh g-1 at 0.1 C over 500 cycles under 60 oC.” Yao said. “The presented ultrathin LLZTO-based film has great potential for practical applications in all-solid-state lithium batteries.”
Yao is also affiliated with the Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Other contributors include Qingya Guo, Fanglin Xu, Lin Shen, Shungui Deng, Zhiyan Wang and Mengqi Li all with Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, CAS. Shen and Wang are also affiliated with the Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
The National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2018YFB0905400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. U1964205, U21A2075, 51872303, 51902321), Ningbo S&T Innovation 2025 Major Special Programme (Grant Nos. 2019B10044, 2021Z122), Zhejiang Provincial Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2022C01072) and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (Y2021080) supported this work.
###
Reference
Authors: Qingya Guo,1 Fanglin Xu,1 Lin Shen,1,2 Shungui Deng,1 Zhiyan Wang,1,2 Mengqi Li,1 and Xiayin Yao1,2
Title of original paper: 20 μm-Thick Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12-based flexible solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries
Journal: Energy Material Advances
DOI: 10.34133/2022/9753506
Affiliations:
1Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201, China
2Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
About the author:
Xiayin Yao is a professor at Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIMTE, CAS). He received Ph.D. from Institute of Solid-State Physics and NIMTE, CAS in 2009. After that, he joined NIMTE and worked there until now. He worked as a research fellow or a visiting scholar in Hanyang University, Republic of Korea (2012–2013), Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (2013–2014) and the University of Maryland, College Park, USA (2018–2019). So far, he has co-authored over 160 peer-reviewed journal papers and applied more than 60 Chinese patents. His major interests include developing solid-state electrolytes with high ionic conductivities, solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries as well as solid-state sodium batteries.
Journal
Energy Material Advances
DOI
10.34133/2022/9753506
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
20 μm-Thick Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12-based flexible solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries
Article Publication Date
4-Jul-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.




