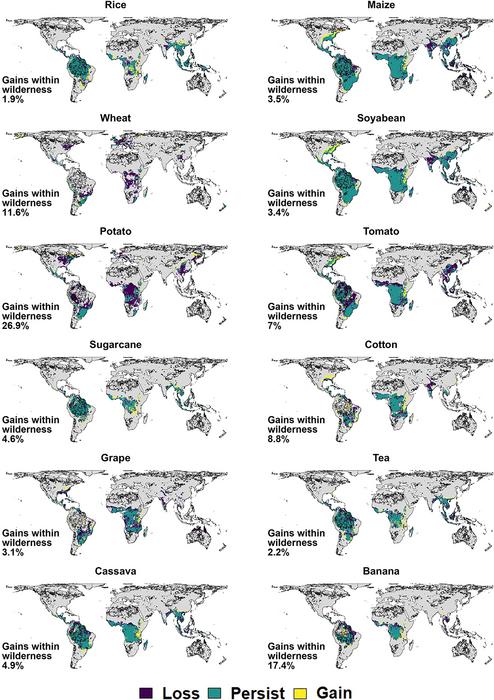
Expansions in crop farming across the globe are the biggest driving force of biodiversity loss in the wild. Now, in a new study publishing in the journal Current Biology on November 6, researchers have modeled how the world’s agricultural landscape could change over the next 40 years. By pulling information on 1,708 crops from a database created by the Food and Agricultural Organization, they predict that as global temperatures rise, wilderness areas closer to the earth’s poles will become newly suitable for growing crops, placing these valuable ecosystems at risk.
Credit: Current Biology/Gardner et al.
Expansions in crop farming across the globe are the biggest driving force of biodiversity loss in the wild. Now, in a new study publishing in the journal Current Biology on November 6, researchers have modeled how the world’s agricultural landscape could change over the next 40 years. By pulling information on 1,708 crops from a database created by the Food and Agricultural Organization, they predict that as global temperatures rise, wilderness areas closer to the earth’s poles will become newly suitable for growing crops, placing these valuable ecosystems at risk.
“We expected that warming temperatures would increase agricultural suitability at high latitudes,” says lead author Alexandra Gardner (@AlexandraGardnr) of the University of Exeter, “but the scale of this result, and the extent to which this newly suitable land is in wilderness, was surprising: 76% of newly suitable land at high latitudes is currently wilderness, equivalent to 10% of the total wilderness in these areas.”
This statistic means that much of the wilderness is at risk of being significantly harmed as global temperatures rise and humans are forced to seek out environments conducive to high crop yield. Currently, many of the world’s crops are cultivated in regions closer to the equator, which is an area that is already experiencing a loss of wilderness due to agriculture. The researchers predict that over the next 40 years, 72% of land currently suitable for agricultural use will go through a loss of biodiversity as higher-latitude regions become warmer and therefore more suitable for agriculture.
Scientists estimate that since the early 1990s, 3.3 million square kilometers of wilderness—an area roughly twice the size of Alaska—have been lost to agricultural activity. Even though many new protected areas have been established since, they have not been enough to keep up with the demand that agriculture places on natural environments.
“We need to understand the specific impacts of different agricultural practices on biodiversity,” says Gardner. “An important step is knowing how we can maintain or improve crop yields on existing agricultural land using sustainable practices that do not harm or minimize the negative impacts on natural biodiversity.”
Gardner and colleagues say that a good way to do this is to promote manmade biodiversity by growing a variety of crops that have been tailored to the natural environment on a single farm. This has two important benefits: meshing with the environment so as not to disrupt the natural wildlife and protecting crop yields from the threats of climate change. If the effects of climate change cause one crop to fail while the others survive, the agricultural biodiversity the farmer has planned will mean that both the environment and the farmer’s source of income will be largely preserved.
The researchers note in their paper that strategy and policy must evolve alongside agriculture. “This is never going to be successful unless you bring the farmers into the decision-making process,” says Ilya Maclean (@IlyaMaclean) of the University of Exeter. “What we’ve seen over the last 50 years is a shift toward extensive large fields and monocultures. It’s much cheaper for a farmer to produce crops that way. But if you grow a single crop on your farm, you’re more susceptible to the uncertainties of climate change.”
“What we’ll be seeing is parts of the last untouched places on the planet becoming more suited for agriculture,” says Maclean.
###
This work was supported by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) in partnership with the Cornwall Council.
Current Biology, Gardner et al. “Wilderness areas under threat from global redistribution of agriculture” https://cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(23)01229-0
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit: http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected].
Journal
Current Biology
DOI
10.1016/j.cub.2023.09.013
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Wilderness areas under threat from global redistribution of agriculture
Article Publication Date
19-Oct-2023




