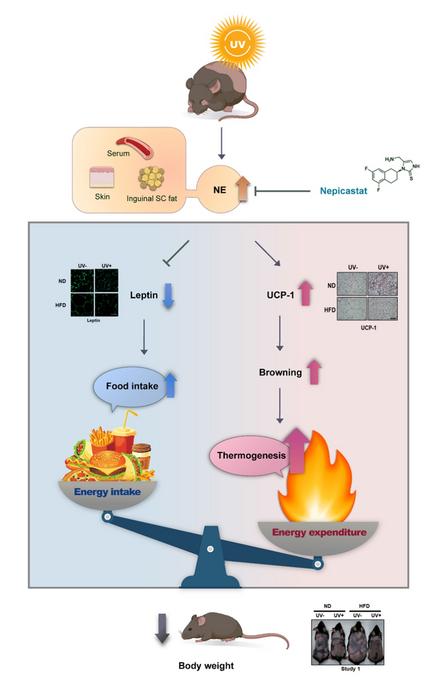
Philadelphia, May 22, 2024 – Obesity and metabolic disorders are increasingly significant global public health issues. In a novel study, a team of dermatologists evaluated the effect of ultraviolet (UV) exposure on appetite and weight regulation. They found that UV exposure raises norepinephrine levels, decreases leptin levels, and induces the browning of subcutaneous fat, thereby increasing energy expenditure. These results potentially pave the way for new approaches to prevent and treat obesity and metabolic disorders. Their findings appear in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier.
Credit: Journal of Investigative Dermatology
Philadelphia, May 22, 2024 – Obesity and metabolic disorders are increasingly significant global public health issues. In a novel study, a team of dermatologists evaluated the effect of ultraviolet (UV) exposure on appetite and weight regulation. They found that UV exposure raises norepinephrine levels, decreases leptin levels, and induces the browning of subcutaneous fat, thereby increasing energy expenditure. These results potentially pave the way for new approaches to prevent and treat obesity and metabolic disorders. Their findings appear in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier.
UV radiation is a common environmental factor that has multifaceted effects on the skin, which encompasses a substantial surface area of the body. UV radiation induces detrimental effects such as sunburn, photoaging, and skin cancer; however, it is also associated with beneficial effects such as vitamin D synthesis.
Co-first authors Qing-Ling Quan, MD, PhD, and Eun Ju Kim, PhD, Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Hospital, explained, “Recent evidence has suggested that UV exposure limits body weight gain in mouse models of obesity. Subcutaneous fat is a critical organ in regulating energy homeostasis. Alongside previous studies on the effects of UV exposure on obesity and metabolic disorders, our team was inspired by our prior discovery that, although UV rays do not directly reach subcutaneous fat when exposed to the skin, they can regulate the metabolism of subcutaneous fat. This led us to hypothesize that skin exposure to UV rays could play a significant role in systemic energy homeostasis, prompting this research.”
Investigators discovered that when exposed to UV radiation consistently, mice fed a normal diet and those on a high-fat diet exhibited increased appetite due to a decrease in leptin, a key hormone in appetite regulation. However, there was no weight increase. They found that UV radiation inhibits weight gain by enhancing secretion of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, which not only decreases leptin but also increases energy expenditure through the “browning” of subcutaneous fat.
The increased energy intake, driven by heightened appetite, is converted to heat and burned before it can accumulate in subcutaneous fat, thus preventing weight gain.
This research provides new insights into the impact of UV exposure on appetite and weight regulation, opening possibilities for novel approaches in the prevention and treatment of obesity and metabolic disorders. Specifically, uncovering the mechanism by which UV radiation prevents weight gain could offer new approaches to dietary regulation and weight loss, providing innovative insights into health and obesity management that could positively impact human health.
Lead investigator Jin Ho Chung, MD, PhD, Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, explained, “This study elucidates the mechanism by which UV exposure can increase appetite while inhibiting weight gain. These findings contribute significantly to understanding the effects of UV radiation on energy metabolism and homeostasis and open new avenues for exploring prevention and treatment strategies for obesity and metabolic disorders. Notably, the fact that UV radiation lowers leptin levels and increases norepinephrine, thereby promoting the browning of subcutaneous fat and increasing energy expenditure, provides a groundbreaking clue for the development of obesity treatment strategies. This research demonstrates that UV exposure not only affects the skin but also plays a deep role in our body’s energy metabolism and homeostasis processes. However, further research is needed on the long-term effects and safety of UV exposure, and there should be significant interest in developing new therapeutic approaches that utilize the efficacy of UV radiation.”
However, as co-corresponding author Dong Hun Lee, MD, PhD, Institute of Human-Environment Interface Biology, Seoul National University, noted, “Because UV exposure can accelerate skin aging and promote skin cancer, it is advisable to minimize UV exposure and protect the skin with sunscreen. Thus, our research team plans to conduct follow-up studies to develop new strategies that could mimic the effects of UV radiation for obesity and metabolic regulation.”
Journal
Journal of Investigative Dermatology
DOI
10.1016/j.jid.2024.03.012
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
UV Irradiation Increases Appetite and Prevents Body Weight Gain through Upregulation of Norepinephrine in Mice
Article Publication Date
22-May-2024




